What is a PaaS?
A platform as a service, or PaaS, is one of the three major cloud computing service models. In our opinion, it’s the only one that successfully delivers all benefits of the cloud to software developers, including control, cost-effectiveness, flexibility, and scalability.
Of course, other as-a-service models are still useful. In fact, all three main cloud computing models offer different advantages to organizations.
Software as a Service, or SaaS, gives you ready-made applications. It’s a popular choice for growth-focused startups, mid-market and enterprise companies, and teams with little to no software development knowledge. On the other hand, Infrastructure as a Service, or IaaS, can be advantageous for those who want more administrative control.
However, for those who wish to streamline developer workflows, deliver products faster, and lower operational costs (all while enriching customization), a PaaS is the way to go. We’ll tell you why.
An overview of platform as a service
The PaaS cloud computing model has several primary use cases. The most common are:
- As an application development platform. Thanks to integrated languages, frameworks and services, developers can use a PaaS to develop, customize, and upgrade cloud-based applications, websites and APIs (application programming interfaces).
- For agile development and DevOps. A PaaS is an alternative to DIY Kubernetes. It provides fully configured environments that automate software application lifecycles and management and creates agile development workflows.
- For analytics and business intelligence (BI). A PaaS often comes equipped with tools that facilitate data analysis and mining. Teams can use this data to identify patterns, anomalies, and trends that drive strategic business decisions.
- For hosting and infrastructure. Developers don’t have to worry about storage, servers, or any other kind of infrastructure with a PaaS. All of these elements are handled by the provider. Nothing needs to be manually set up, you only need to write your code.
But what is a Platform as a Service exactly, and how does it compare to SaaS?
What is a PaaS in cloud computing?
A PaaS is a cloud computing model where a third-party host provides a business with a complete development and deployment platform. It supplies everything necessary for the development and delivery of web applications, automating the whole pipeline.
These resources enable developers to develop, deploy, and manage everything from simple, small-scale applications or websites to advanced and highly customized experiences.
A PaaS can support the entire development lifecycle, from building and testing to the continuous maintenance and updating of applications. This can help clients avoid the expense, inflexibility, and labor-intensiveness of installing and maintaining resources.
In other words, PaaS providers such as Platform.sh build a platform so you don’t have to. They take on the associated costs, time, and risk—all while shouldering the responsibility of ensuring your app or site is available and a working infrastructure is maintained.
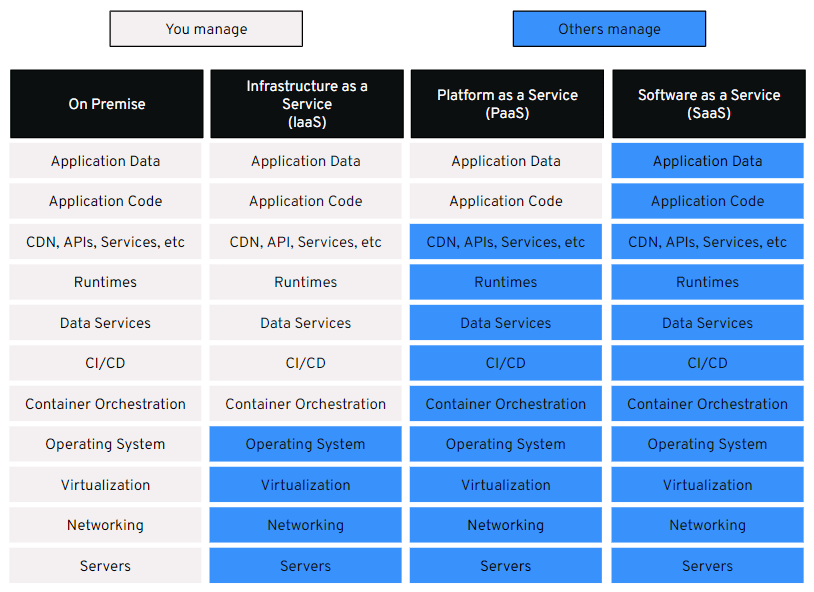
PaaS, IaaS, and SaaS
So, now you have an idea of what a PaaS is and how it works, but how does it compare to the two other main cloud computing models on the market: IaaS and SaaS?
IaaS
Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) provides businesses with the backend IT resources they need (networks, servers, and storage) to manage workloads in the cloud.
IaaS provides a general data center for storage and dynamic scaling capabilities. It can support volatile or evolving applications, and it’s a viable solution for businesses experiencing unpredictable or rapid growth but lacking the finances to invest in backend IT hardware.
Like other as-a-service models, it’s a good choice for companies looking to migrate away from the labor intensity of maintaining on-premise resources.
However, IaaS is the most demanding of these three models. It only delivers infrastructure, leaving you responsible for operating systems, applications, middleware tools, and runtime. Plus, there’s no automation. Even for the most capable teams, this can be a significant drain on labor costs and productivity.
So, if you opt for IaaS exclusively, it should only be because your business goals require extremely high levels of administrative control.
SaaS
Software as a Service (SaaS) refers to a model in which third parties build applications and deliver them to buyers via the internet as either a web application or a downloadable app.
With no restrictions on device or location, SaaS is incredibly popular with global and remote teams. Applications are painless to set up independently and facilitate collaborative working.
Delivering feature-rich, ready-made applications for everything from email, office, and video conferencing to tax and project management, the productivity, workflow, and time-to-value benefits of SaaS are plentiful.
However, SaaS’s ease of use and efficiency come at a cost. Not only do you have no administrative control, but SaaS offers very little in the way of customizability. Its integration capabilities also remain limited.
It’s also vital to remember that just because you use a piece of software, it doesn’t mean you own it. The SaaS provider has complete ownership of the system and your overall control of everything - including data - is severely limited.
If you want any degree of control over your application, either PaaS or IaaS would be a better fit.
PaaS
So, how does a PaaS compare to the other as-a-service models?
A PaaS sits in the center of the cloud computing stack, acting as a middle-ground between IaaS and SaaS. It delivers the customization and flexibility of IaaS but streamlines workflows and improves time-to-market in a similar way to SaaS.
As a result, DevOps teams can maximize their productivity. Unlike IaaS clients, they’re freed from the burden of OS management, software patching, load balancing, and other tasks. But they can also innovate, which is something SaaS clients can’t do.
If you’re curious to learn more , check out this video that explains 10 reasons you need a modern PaaS for your business.
Benefits of a PaaS: From cost-efficiency to scalability
Curious to know what using a PaaS in cloud computing can do for your business? Then let’s explore some of the most valuable benefits, starting with a favorite: scalability.
Scalability
Some platforms require you to anticipate growth and scale up by buying expensive additional tooling. But if you don’t achieve that sustainable growth you expected, you end up with idle resources that drain cash flows and productivity, and that can seriously limit your operative productivity and reduce your bottom line.
With a PaaS, you can purchase additional resources as you experience traffic spikes and deploy these for immediate effectiveness. If your traffic drops again, you can automatically scale back down with zero hassle.
Moreover, a PaaS allows this scalability to be applied across multiple apps and websites when needed. Multi-app scaling makes using a PaaS particularly efficient for businesses with several apps or a fleet of websites.
End-to-end cost-efficiency
Hosting requires significant capital investment into multiple resources. PaaS consolidates these resources and delivers them via one pay-as-you-grow model, meaning that start-ups and small businesses can forgo the expenses that come with building their own platform.
While IaaS is also cost-effective, it can generate unexpected costs if you’re not careful.
But unlike IaaS, PaaS providers handle maintenance, security patches, and updates, which reduces labor costs and other expenses that can creep up, like tooling costs.
Improved productivity and time efficiency
Having immediate access to a fully equipped development environment empowers developers to build high-quality applications faster and more reliably. Without the need to build, install, and configure a backend infrastructure, your developers can seamlessly integrate with the development environment.
This enables them to get started straight away, speeding up your time-to-market.
Greater flexibility
Developers can access the shared software development environment from any location, improving remote working accessibility and collaborative productivity.
No vendor lock-in
Advanced PaaS providers are cloud-agnostic solutions. Platform.sh, for example, is a multi-cloud option that uses open-source software to allow teams to migrate and operate workloads to different vendors without needing to undergo refactoring.
Built-in security and compliance
Abiding by strict security, privacy, and compliance requirements is a struggle with on-premise and even IaaS solutions. PaaS providers relieve you of this labor-intensive task by providing built-in security and compliance features across your cloud environment.
Armed with compliance certifications, encryptions, access controls, patching, updates, and a host of other security measures, you can achieve reliable technical and organizational-level security.
Key PaaS solutions to consider
So, what should you look for in a modern cloud Platform-as-a-Service solution? While your needs will vary depending on your business, there are a few essential features to look out for.
Design, testing, and development tools
First and foremost, look at the development tools offered by the PaaS provider. As a rule, it should provide an integrated toolchain of all the essential tools you need to successfully build an application, including a source code editor, debugger, and compiler.
Observability
Optimal performance and user experience for your websites and applications are crucial. The observability tools offered by a PaaS provider should give you actionable insights to improve your code and supply comprehensive performance monitoring. They should provide you with a real-time view of your resource usage and offer flexible scaling.
Security and compliance
Your PaaS solution must help you keep your website or application safe, secure, and available at all times. It should offer protection from cyberattacks and comply with the numerous data security and privacy standards worldwide. Consider how your prospective provider handles data retention and backups and recoveries. Make sure your chosen solution takes security and compliance as seriously as you do.
Databases
A PaaS should have centralized database management capabilities and tools. It also allows developers to create, query, and maintain databases.
Infrastructure
A PaaS should have the same infrastructure offerings as IaaS: supplying and maintaining storage, servers, and network components.
Scale your apps with a preferred PaaS
Effortlessly develop, deploy, and scale your enterprise-grade websites and applications with Platform.sh—a unified and secure multi-cloud scalable PaaS.
We believe it’s critical for companies to develop agile fitness in fast-paced business climate. We offer robust PaaS protection, future-proofing your enterprise in the face of uncertainty.
Along with a fully-built infrastructure, our solution handles everything from data management to provisioning, auto-scaling, testing, observability, and security.
Unlike many other PaaS providers, Platform.sh is a polyglot, multi-cloud platform. We support more than 100 frameworks and 10 programming languages, so you can build exactly how you want. PHP? Java? React? Ruby? Drupal? If you can name it, you can build with it.
Eliminating the need to build and manage infrastructure allows you to leverage faster deployment, sustainable scaling, and innovative, collaborative development. Instead of worrying about infrastructure, your developers can concentrate on what matters most—creating incredible applications that meet your customers’ needs.
Some happy PaaS customers
With 7,000 customers and over 17,000 developers using the Platform.sh Platform-as-a-Service, there are plenty of examples of development teams reaping the benefits that our PaaS can bring.
The University of Missouri, a renowned higher-ed institution in the US, achieved a 300% increase in their Drupal and WordPress sites’ request handling capabilities and a 30% reduction in annual hosting costs after making the switch to a PaaS. You can learn more about how they made these impressive gains in their case study.
SportRx, an athletic eyewear brand, was on the hunt to find a scalable development solution to help meet a 40% annual growth goal. They needed high performance during heavy traffic—particularly when it came to sales season—and after adopting the Platform.sh PaaS, they welcomed 80% fewer support requests due to problems with their website. They also enhanced team efficiency as the average time to install weekly software updates dropped from an hour to 15 minutes—a 75% decrease. Learn more about how they did this in their case study.
Global digital agency, Burst, needed a single, scalable global digital marketing platform that provided website consistency and governance worldwide while extending flexibility, speed, and creativity to 50 local marketing managers for their client, Mentos. By using the Platform.sh PaaS, the Burst team reduced hosting costs by 60% and eliminated the need for and costs associated with 2 DevOps FTE in developing their platform vision and multi-app strategy for the Mentos team. Find out how in their case study.
Check out some more PaaS customer success stories.
FAQ
Can PaaS solutions be used for mobile application development?
Yes, PaaS solutions can be used for mobile application development. Many PaaS providers offer tools and frameworks specifically designed for mobile application development, including support for popular languages and environments.
How does a PaaS handle data backup and recovery?
PaaS providers typically offer automated data backup and recovery services as part of their platform. These services include regular backups, data snapshots, and disaster recovery plans to ensure data integrity and availability. Developers can usually configure backup frequency and retention policies to align with their specific requirements, ensuring that data can be restored quickly in case of data loss or corruption.
What are some common challenges businesses face when adopting a PaaS?
Common challenges when adopting a PaaS include overcoming the learning curve for new tools and environments, ensuring compatibility with existing systems, managing data migration, addressing security and compliance concerns, and preventing vendor lock-in. Organizations must also adjust their development and operational processes to fully leverage the benefits of a PaaS, which can require significant changes in workflow and culture.
Can a PaaS be used for AI and machine learning applications?
Yes, a PaaS can be used for AI and machine learning (ML) applications. Many PaaS providers offer specialized services and frameworks for AI and ML, such as pre-configured environments for training models, scalable computing resources for processing large datasets, and integration with popular libraries like TensorFlow, PyTorch, and Scikit-learn. These platforms simplify the deployment and management of AI and ML models, enabling developers to focus on innovation.
What is the typical learning curve for developers new to PaaS?
The learning curve for developers new to PaaS can vary based on their familiarity with cloud computing and the specific platform in use. Generally, developers need to learn how to navigate the PaaS environment, utilize provided tools and services, and understand the deployment and scaling processes. Many PaaS providers offer extensive documentation, tutorials, and training resources to help developers get up to speed quickly.
Can PaaS solutions be customized to meet specific business needs?
Yes, PaaS solutions can be customized to meet specific business needs. Developers can choose from a variety of languages, frameworks, and tools supported by the PaaS provider to build and deploy applications that align with their requirements. Additionally, many PaaS platforms offer configuration options and APIs that allow further customization of the environment, integration with other services, and tailoring of workflows.
How do PaaS solutions handle software updates and patches?
PaaS solutions typically handle software updates and patches automatically. The PaaS provider is responsible for maintaining the underlying infrastructure, including applying updates to operating systems, middleware, and security patches. This ensures that the platform remains secure and up-to-date without requiring manual intervention from developers, allowing them to focus on building and deploying applications.
Is it possible to migrate existing applications to a PaaS?
Yes, it is possible to migrate existing applications to a PaaS. The migration process typically involves several steps, including assessing the current application architecture, choosing a suitable PaaS provider, modifying the application to meet the PaaS requirements, and testing the application in the new environment. Tools and services offered by PaaS providers, such as migration assistants and compatibility checks, can facilitate this process and ensure a smooth transition.
How does a PaaS support microservices architecture?
PaaS supports microservices architecture by providing a scalable and flexible environment where individual services can be developed, deployed, and managed independently. PaaS platforms often include features such as container orchestration (e.g., Kubernetes), service discovery, API gateways, and integrated development tools that facilitate the creation and maintenance of microservices. This approach allows for easier scaling, resilience, and updates of each service component.
 Switching to Platform.sh can help IT/DevOps organizations drive 219% ROI
Switching to Platform.sh can help IT/DevOps organizations drive 219% ROI Organizations, the ultimate way to manage your users and projects
Organizations, the ultimate way to manage your users and projects